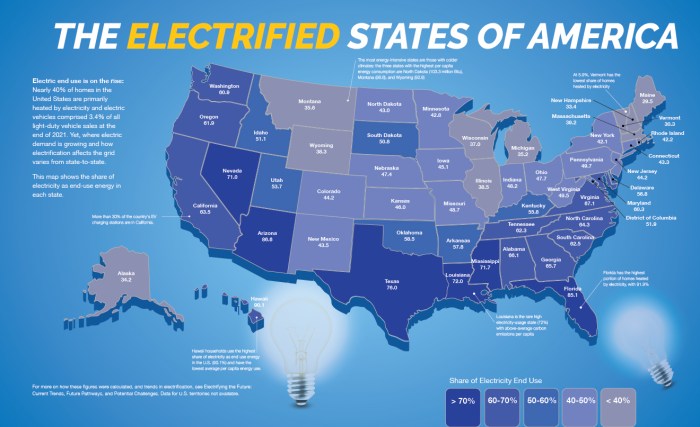
Disaster recovery is crucial for any organization, ensuring business continuity in unforeseen events. A key aspect of this planning is understanding Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO). These metrics define the acceptable amount of data loss and downtime in case of a disaster, guiding decisions on data backup, recovery strategies, and technology selection.
This discussion delves into the intricacies of RPO and RTO, exploring their definitions, the factors influencing their determination, and the steps involved in establishing and measuring them. We’ll examine the impact of different technologies, including cloud-based and hybrid environments, on these crucial metrics. Ultimately, this comprehensive guide aims to equip readers with the knowledge to effectively integrate RPO and RTO into their disaster recovery strategies.
Defining RPO and RTO
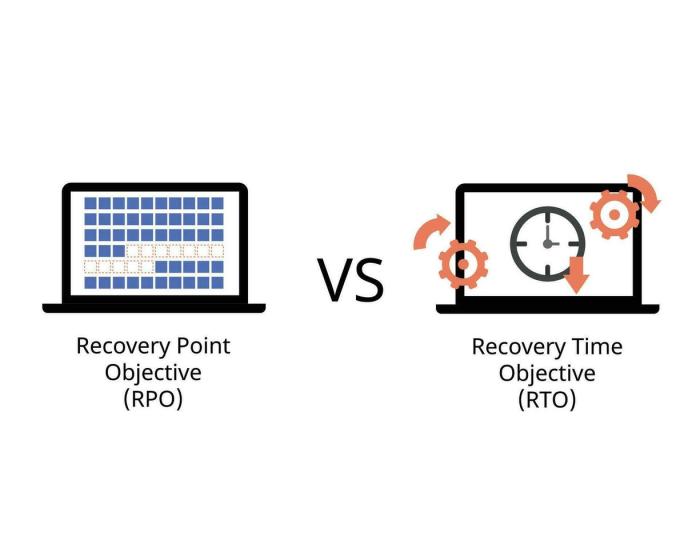
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) are crucial components of disaster recovery planning. Understanding these metrics is vital for businesses to ensure they can quickly and effectively restore operations following a disruption. A well-defined RPO and RTO will help determine the level of data and service restoration required in the event of a system failure or other catastrophic event.Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) are key performance indicators used to measure the success of disaster recovery plans.
They are crucial for defining the acceptable level of data loss and downtime following a disruption. By establishing clear RPO and RTO targets, businesses can prioritize resources and develop effective recovery strategies.
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) Definition
The Recovery Point Objective (RPO) defines the maximum acceptable amount of data loss that a business is willing to tolerate after a disaster. It represents the point in time to which data must be recovered. RPO is measured in terms of time, typically expressed as the period of time that has passed since the last data backup. For example, an RPO of 24 hours means that data loss is acceptable up to 24 hours before the disaster occurred.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) Definition
The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the maximum acceptable time it takes to restore critical business operations after a disaster. This includes the time to recover data, rebuild systems, and bring the business back to its pre-disaster state. RTO is a critical measure of the speed and efficiency of the disaster recovery plan. For instance, an RTO of 4 hours means the business must be fully operational again within four hours of the disaster occurring.
Relationship Between RPO and RTO
RPO and RTO are closely related, but they address different aspects of disaster recovery. RPO focuses on data loss, while RTO focuses on the time it takes to restore operations. An organization needs to carefully balance the RPO and RTO, as a lower RPO often leads to a higher RTO, and vice versa. Compromising one might negatively impact the other, requiring careful consideration of business priorities and resource allocation.
Significance of RPO and RTO in Business Continuity
RPO and RTO are critical components of a robust business continuity plan. By establishing clear RPO and RTO targets, organizations can ensure that they can resume operations as quickly and effectively as possible following a disaster. This minimizes disruption to business operations, maintains customer confidence, and protects the organization’s reputation. Clear objectives allow for appropriate resource allocation and preparation.
Comparison of RPO and RTO Impact on Business Operations
RPO and RTO have a significant impact on business operations. A lower RPO, meaning less data loss, often translates to a higher RTO, meaning a longer recovery time. Conversely, a lower RTO, meaning faster recovery, usually translates to a higher RPO, meaning more acceptable data loss. Businesses need to evaluate their specific needs and balance these factors to create a disaster recovery plan that meets their requirements.
Consider the potential cost of data loss versus the cost of downtime.
Comparison Table of RPO and RTO
| Feature | Recovery Point Objective (RPO) | Recovery Time Objective (RTO) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The maximum acceptable amount of data loss after a disaster. | The maximum acceptable time to restore critical business operations after a disaster. |
| Focus | Data Loss | Time to Recovery |
| Measurement | Time (e.g., hours, days) | Time (e.g., hours, minutes) |
| Impact on Business | Loss of data can lead to revenue loss, operational inefficiencies, and reputational damage. | Downtime can result in lost revenue, customer dissatisfaction, and disruption of business processes. |
Factors Influencing RPO and RTO
Understanding the factors influencing Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is crucial for establishing effective disaster recovery strategies. These objectives are not static; they are dynamic, adapting to changing business needs and technological advancements. Their determination is a collaborative effort between IT and business stakeholders, ensuring a balanced approach to minimizing downtime and data loss.The precise values for RPO and RTO are contingent upon various factors, which will be explored in detail.
This encompasses business priorities, technological considerations, and industry-specific requirements. Understanding these factors will help organizations establish appropriate objectives, enabling a well-structured and efficient disaster recovery plan.
Factors Affecting RPO Determination
Several factors influence the determination of RPO. Data loss tolerance and the criticality of data are key determinants. Organizations need to consider the impact of data loss on business operations, financial performance, and regulatory compliance. For instance, a company handling sensitive customer data may have a lower tolerance for data loss than a company handling less sensitive information.
The frequency of data backups and the effectiveness of data recovery procedures also play a crucial role in determining the acceptable RPO. A robust backup and recovery strategy ensures that data loss is minimized, enabling a lower RPO.
Factors Affecting RTO Determination
Determining the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) involves evaluating various factors. The business impact of downtime, the availability of critical resources, and the level of service expected by customers all contribute significantly to establishing an appropriate RTO. For example, an e-commerce platform might have a much lower tolerance for downtime than a manufacturing plant, as the former’s revenue generation is directly tied to its availability.
The complexity of the recovery process and the availability of personnel and resources to execute the recovery also influence the RTO. Organizations need to assess the time required for various recovery tasks, including system restoration, data recovery, and employee retraining.
Business Priorities Influencing RPO and RTO
Business priorities play a critical role in determining RPO and RTO values. The criticality of specific business functions directly affects the tolerance for data loss and downtime. For example, financial institutions, where transaction processing is paramount, might require very low RPO and RTO values. Similarly, healthcare organizations, where patient data integrity is crucial, need stringent RPO and RTO values.
Balancing business needs with the cost of disaster recovery is essential. A detailed cost-benefit analysis should be performed to ensure the chosen RPO and RTO values are justifiable and achievable.
Role of Technology in Determining RPO and RTO
Technology significantly impacts RPO and RTO. The availability and capabilities of data backup and recovery technologies, such as cloud storage and replication tools, directly influence the achievable RPO and RTO. Advanced technologies, including automated recovery solutions and real-time data replication, can significantly reduce the recovery time. Furthermore, the efficiency and reliability of the IT infrastructure directly impact the organization’s ability to meet its RPO and RTO goals.
Examples of RPO and RTO Values for Various Industries
Different industries have different needs and priorities regarding data loss and downtime. These differing needs often dictate unique RPO and RTO values. For example, a financial institution might target an RPO of hours or even minutes, and an RTO of hours. In contrast, a small retail business might have a higher tolerance for data loss and downtime, with an RPO of days and an RTO of days or even weeks.
Correlation Between Industry and Typical RPO/RTO Values
| Industry | Typical RPO (in hours) | Typical RTO (in hours) |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Services | Few | Few |
| Healthcare | Few | Few |
| Retail | Days | Days |
| Manufacturing | Days | Days |
| E-commerce | Few | Few |
This table provides a general guideline. Specific values will vary based on the unique characteristics and priorities of each organization within an industry.
Developing Disaster Recovery Strategies
Disaster recovery strategies are critical for ensuring business continuity in the face of disruptive events. A well-defined strategy, aligned with Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO), is essential for minimizing data loss and downtime. This section delves into the practical aspects of crafting effective disaster recovery plans.Aligning disaster recovery strategies with RPO and RTO is paramount for a successful outcome.
These objectives, defining acceptable data loss and downtime, must be integral to every phase of the strategy. Failure to align can lead to inefficient resource allocation and an inability to meet business needs during a disruption.
Aligning Disaster Recovery Strategies with RPO and RTO
A well-defined disaster recovery strategy is predicated on a thorough understanding of RPO and RTO requirements. This understanding should guide all decisions regarding data backup, recovery mechanisms, and potential fallback solutions. Strategies must be designed to minimize the impact of disruptions, ensuring that business operations can resume as quickly as possible with minimal data loss.
Mitigation Strategies for RPO and RTO Influencing Factors
Identifying and mitigating risks that impact RPO and RTO is crucial. This involves a comprehensive risk assessment process, identifying potential threats, and developing mitigation plans. The assessment should include potential hazards like natural disasters, cyberattacks, or equipment failures. Robust strategies must be in place to ensure compliance with established RPO and RTO targets. This includes contingency planning, redundant infrastructure, and proactive security measures.
Technology Selection for Meeting RPO and RTO
Selecting appropriate technologies is vital for meeting RPO and RTO requirements. The choice of technology must consider the specific needs of the business, including the volume of data, the sensitivity of the data, and the acceptable level of downtime. A balance must be struck between cost-effectiveness and functionality. Consider factors such as backup frequency, data compression techniques, and recovery speed when making technology selections.
Backup and Recovery Technology Selection Procedure
Selecting backup and recovery technologies involves a structured procedure. First, a thorough analysis of current systems and data is performed. Next, evaluation of potential technologies against established RPO and RTO requirements is critical. The selection process must involve testing and validation to ensure compatibility and efficacy. This includes realistic simulations to gauge performance and identify potential bottlenecks.
The Role of Testing in Ensuring RPO and RTO Compliance
Regular testing is paramount for ensuring compliance with RPO and RTO targets. Testing should encompass both routine backups and full-scale disaster recovery exercises. These tests should be simulated, mimicking real-world disaster scenarios to assess the effectiveness of the disaster recovery plan. This allows for the identification and correction of potential weaknesses and ensures the strategy is robust and reliable.
Realistic testing helps prevent costly errors during an actual disaster.
Disaster Recovery Strategies and Their Impact on RPO and RTO
| Disaster Recovery Strategy | Impact on RPO | Impact on RTO |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Site | High data loss potential | High recovery time |
| Warm Site | Moderate data loss potential | Moderate recovery time |
| Hot Site | Minimal data loss potential | Minimal recovery time |
| Cloud-based Disaster Recovery | Minimal data loss potential | Variable recovery time (depending on cloud provider and configuration) |
| Hybrid Disaster Recovery | Customizable data loss potential | Customizable recovery time |
Measuring RPO and RTO Performance
Effective disaster recovery hinges on accurately measuring and monitoring the performance of RPO and RTO strategies. Regular evaluation ensures that recovery plans remain relevant and effective in addressing potential disruptions. This section details methods for assessing RPO and RTO compliance, emphasizing the crucial role of testing and validation.
Methods for Measuring RPO and RTO Effectiveness
Accurate measurement of RPO and RTO effectiveness involves a multifaceted approach. This includes detailed documentation, rigorous testing, and ongoing monitoring to ensure that the recovery process meets established objectives. Key elements in this process include the identification of specific metrics and the use of appropriate monitoring tools.
Monitoring RPO and RTO Compliance
Continuous monitoring of RPO and RTO compliance is vital for ensuring that the disaster recovery plan remains aligned with business needs. This involves tracking key metrics, conducting regular tests, and promptly addressing any deviations from established targets. Robust monitoring systems provide real-time insights into the recovery process.
Importance of Regular Testing and Validation
Regular testing and validation of RPO and RTO strategies are crucial for ensuring that the recovery plan is functional and reliable. Simulated disaster scenarios provide valuable insights into potential weaknesses and allow for proactive adjustments. This iterative process ensures that the plan remains up-to-date and capable of meeting business requirements.
Metrics for Evaluating Disaster Recovery Performance
Evaluating disaster recovery performance requires a set of measurable metrics that accurately reflect the plan’s effectiveness. These metrics should encompass various aspects of the recovery process, including data restoration time, system restoration time, and user access. The metrics should be specific and quantifiable to provide a clear picture of the recovery plan’s performance.
Metrics for Assessing RPO and RTO Compliance
- Data Recovery Time Objective (DRTO): The maximum acceptable time to restore data after a disaster. This metric is crucial for ensuring business continuity and minimizing data loss.
- System Recovery Time Objective (SRTO): The maximum acceptable time to restore the entire system after a disaster. This metric ensures that critical applications and services are available in a timely manner.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): The maximum acceptable amount of data loss after a disaster. This metric is critical for businesses that rely heavily on data integrity.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): The maximum acceptable time to resume normal business operations after a disaster. This metric directly impacts revenue and customer satisfaction.
- Test Success Rate: The percentage of successful disaster recovery tests conducted. This metric reflects the reliability and effectiveness of the recovery plan in real-world scenarios.
- Number of Recovery Incidents: The frequency of recovery events. A high number might indicate inadequacies in the disaster recovery plan or its execution.
Monitoring Tools for RPO and RTO
Choosing appropriate monitoring tools is crucial for tracking RPO and RTO compliance. These tools should provide real-time visibility into the recovery process, allowing for prompt identification and resolution of potential issues. This proactive approach ensures that the disaster recovery plan remains effective and reliable.
| Monitoring Tool | Description | Features |
|---|---|---|
| ServiceNow | A comprehensive IT service management platform. | Incident management, change management, and reporting capabilities. |
| SolarWinds | A suite of monitoring tools for IT infrastructure. | Provides detailed monitoring of servers, networks, and applications. |
| Datadog | A cloud-based monitoring and analytics platform. | Real-time monitoring and alerting for applications and infrastructure. |
| Nagios | Open-source monitoring tool for servers and networks. | Alerting and reporting for system performance and availability. |
RPO and RTO in Cloud Environments
Cloud computing has revolutionized disaster recovery, offering significant advantages over traditional on-premises solutions. This shift necessitates a nuanced understanding of how Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) are impacted and managed within cloud-based environments. The inherent flexibility and scalability of cloud platforms provide unique opportunities for optimizing disaster recovery strategies, yet also present new considerations for establishing effective RPO and RTO targets.Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions often leverage the inherent redundancy and geographically distributed nature of cloud infrastructure.
This allows for rapid failover and restoration of services, potentially enabling faster recovery times and lower data loss compared to on-premises solutions. The inherent elasticity of cloud resources enables organizations to adjust their recovery capacity based on changing business needs, contributing to greater agility and efficiency.
Implications of Cloud Computing on RPO and RTO
Cloud environments offer significant flexibility in defining and achieving RPO and RTO targets. The availability of geographically distributed data centers and redundant infrastructure within cloud platforms contributes to faster recovery times and reduced data loss. This resilience is a key factor in achieving stringent RPO and RTO requirements.
How Cloud-Based Solutions Influence RPO and RTO
Cloud-based solutions can dramatically influence RPO and RTO by enabling rapid deployment of disaster recovery resources. Automated failover mechanisms, built into cloud services, can trigger instant restoration of applications and data in the event of a disaster. This significantly reduces recovery time compared to traditional on-premises solutions. Furthermore, cloud-based solutions often incorporate features that automatically replicate data, minimizing data loss in the event of a disaster.
Benefits of Using Cloud-Based Solutions for Disaster Recovery
Cloud-based solutions offer several key advantages for disaster recovery:
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud resources can be provisioned or de-provisioned dynamically, allowing organizations to adjust their recovery capacity based on changing business needs and workload fluctuations. This adaptability is crucial in a constantly evolving business landscape.
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud-based solutions often eliminate the need for significant upfront capital investment in hardware and infrastructure. Organizations can pay only for the resources they utilize, leading to significant cost savings compared to traditional on-premises solutions. This is especially true during non-peak usage.
- Faster Recovery Times: Automated failover mechanisms and the inherent redundancy of cloud infrastructure enable organizations to restore services rapidly, minimizing downtime and business disruption.
- Reduced Data Loss: Cloud-based solutions frequently incorporate automated data replication, significantly reducing data loss in the event of a disaster.
Considerations for Establishing RPO and RTO in a Cloud Environment
Several considerations are crucial when establishing RPO and RTO targets in a cloud environment:
- Data Replication Strategy: Selecting the appropriate data replication strategy is critical. This includes factors like frequency, method, and location of replication to ensure data consistency and availability.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Carefully review the SLAs offered by the cloud provider to understand their commitments regarding recovery time and data loss.
- Testing and Validation: Thorough testing and validation of disaster recovery plans are essential to ensure that cloud-based solutions meet the required RPO and RTO targets. Regular testing exercises are vital to ensure disaster recovery plan effectiveness.
- Security Considerations: Cloud security is crucial, and robust security measures must be implemented to protect data and applications during and after a disaster.
Comparing RPO and RTO in On-Premises and Cloud-Based Environments
| Factor | On-Premises | Cloud-Based |
|---|---|---|
| RPO | Defining RPO often involves manual data backups and restoration procedures, which can impact the recovery process. | Cloud providers frequently offer automated data replication, enabling faster recovery and reduced data loss. |
| RTO | RTO is typically affected by the time required for deploying and configuring recovery resources, which can be significant. | Automated failover mechanisms in cloud environments enable faster recovery times. |
The table illustrates how cloud environments often offer faster and more automated recovery processes compared to on-premises environments.
Calculating RPO and RTO for a Cloud-Based Application
Calculating RPO and RTO for a cloud-based application involves similar principles to on-premises systems, but with a different approach due to automation.
Example: An organization decides to replicate their database every 15 minutes to a geographically separate cloud region. In the event of a disaster, they can restore the database from the last successful 15-minute replication.
The time to restore the application to full functionality will depend on the cloud provider’s failover procedures. A cloud provider’s documentation will often provide specifics about RPO and RTO capabilities. The organization should utilize this documentation to establish realistic RPO and RTO targets and then implement comprehensive testing procedures to validate their disaster recovery plan.
RPO and RTO in Hybrid Environments

Hybrid environments, combining on-premises and cloud-based infrastructure, present unique challenges and opportunities for disaster recovery planning. Understanding how RPO and RTO interact in these multifaceted systems is crucial for effective business continuity. The interplay between different technologies and the need for seamless data synchronization and application availability demands careful consideration of recovery strategies.Hybrid environments necessitate a comprehensive approach to RPO and RTO management.
This includes careful planning for data replication, application migration, and system failover between on-premises and cloud components. Strategies must address the potential for varying performance characteristics across the different environments.
Implications of Hybrid Environments on RPO and RTO
Hybrid environments introduce complexities in defining and achieving acceptable RPO and RTO targets. The varying performance characteristics of on-premises and cloud infrastructure can impact the overall recovery time and point objectives. For example, an on-premises system might have faster recovery capabilities for specific applications, while the cloud might excel in handling high-volume data replication. Understanding these differences is critical for developing a robust hybrid recovery strategy.
Complexities of Establishing RPO and RTO in a Hybrid Environment
Establishing consistent RPO and RTO targets across on-premises and cloud-based systems in a hybrid environment presents several challenges. The varying infrastructure characteristics (e.g., network latency, bandwidth limitations) and the different recovery mechanisms used in each environment contribute to this complexity. Furthermore, integrating different systems and applications can introduce complexities in data synchronization and application availability.
RPO and RTO Strategies for Hybrid Environments
Effective RPO and RTO strategies for hybrid environments often involve a tiered approach. Applications critical for business operations might have stricter RPO/RTO targets and be prioritized for recovery on the more resilient on-premises infrastructure. Less critical applications could be recovered faster from the cloud. This approach allows for balancing cost-effectiveness with business needs.
Maintaining Consistency Across On-Premises and Cloud-Based Systems
Maintaining consistent RPO and RTO performance across on-premises and cloud-based systems requires careful planning and execution. Data replication and synchronization between environments are critical. Ensuring that applications function seamlessly in both environments and that failover procedures are well-defined and tested is crucial. Automated testing and validation of recovery procedures are vital to ensure reliable performance.
Integrating RPO and RTO Across Different Systems
Integrating RPO and RTO targets across various systems in a hybrid environment requires a centralized management system. This system should monitor the performance of different systems, track recovery progress, and provide real-time alerts. The system should also be capable of adjusting recovery strategies based on real-time conditions. A robust monitoring system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance during recovery.
Process of Implementing RPO and RTO in a Hybrid Environment
The following flowchart illustrates the process of implementing RPO and RTO in a hybrid environment. This structured approach allows for a standardized process across different systems.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Define RPO/RTO targets for all applications and systems. |
| 2 | Assess the performance characteristics of on-premises and cloud infrastructure. |
| 3 | Design data replication and synchronization strategies. |
| 4 | Develop failover procedures for different systems and applications. |
| 5 | Implement monitoring and alerting systems. |
| 6 | Test and validate recovery procedures. |
| 7 | Regularly review and update recovery plans. |
Illustrative Examples
Understanding RPO and RTO requires practical application. Illustrative examples demonstrate how these concepts translate into real-world scenarios, highlighting the critical importance of establishing appropriate recovery strategies. This section delves into specific examples, outlining the considerations for varying situations and emphasizing the significance of regular policy reviews.
Example of a Company Requiring Strict RPO and RTO
A financial institution, handling sensitive customer data, faces significant regulatory compliance requirements. Their business-critical systems must maintain minimal data loss and rapid recovery. A strict RPO of near-zero data loss and an RTO of a few hours is essential. Failure to meet these targets would lead to severe financial penalties, reputational damage, and potential legal ramifications. This underscores the importance of implementing robust disaster recovery solutions, including redundant data centers, automated failover mechanisms, and well-trained personnel.
Successful Disaster Recovery Implementation
A large e-commerce company, experiencing significant growth, implemented a multi-tiered disaster recovery strategy. They established a geographically dispersed data center network, ensuring continuous operation during potential disruptions. Their RPO was set at a few minutes of lost transactions, while their RTO was designed for under 24 hours. This robust system enabled them to maintain customer confidence and operational efficiency during a severe hurricane, demonstrating the value of proactive disaster preparedness.
Procedures to Address Risks Associated with Specific RPO and RTO Values
To mitigate risks associated with specific RPO and RTO values, a comprehensive risk assessment is crucial. This assessment must evaluate the potential impact of various disruptions on business operations and identify vulnerabilities. Procedures should be documented to guide recovery actions. These should include detailed failover procedures, communication protocols, and training for staff. For instance, a low RPO and RTO necessitates the use of backup systems, redundancy, and fast recovery mechanisms.
Regular testing and simulation are paramount to verifying the efficacy of the procedures.
Importance of Regular Review of RPO and RTO Policies
Regular review of RPO and RTO policies is critical to maintaining the effectiveness of disaster recovery strategies. Business needs evolve over time, potentially requiring adjustments to recovery targets. Technology advancements also necessitate reevaluation of existing policies. This proactive approach ensures the company’s recovery strategy remains aligned with current business objectives and regulatory requirements.
Impact of Regulatory Compliance on RPO and RTO
Regulatory compliance often dictates the required RPO and RTO values. Industries like finance, healthcare, and government are subject to stringent regulations concerning data protection and business continuity. These regulations Artikel specific requirements for data backup, recovery, and system availability. Non-compliance can lead to substantial fines, legal issues, and damage to reputation. For example, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) mandates specific RPO and RTO requirements for companies handling credit card information.
Case Study: Successful RPO and RTO Implementation (HTML)
| Company | Industry | RPO | RTO | Recovery Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Manufacturing | Automotive | 0 minutes | 2 hours | Redundant data centers, automated failover to secondary site, 24/7 monitoring |
| XYZ Healthcare | Medical | 1 day | 48 hours | Cloud-based backup and recovery, remote access to critical systems |
ABC Manufacturing, an automotive parts manufacturer, experienced a significant data loss incident. To prevent similar issues in the future, they implemented a comprehensive disaster recovery strategy that included redundant data centers and automated failover. The successful implementation ensured minimal downtime, preserving their operational efficiency. The RPO and RTO values were crucial in minimizing the impact of the incident and safeguarding the company’s reputation.
XYZ Healthcare, a large medical facility, prioritized patient safety and data security. They opted for a cloud-based disaster recovery solution, enabling them to quickly recover their critical systems and maintain operations. This approach provided a robust framework for data protection and business continuity. The successful implementation showcased the flexibility and scalability offered by cloud-based solutions for achieving specific RPO and RTO values.
Ending Remarks
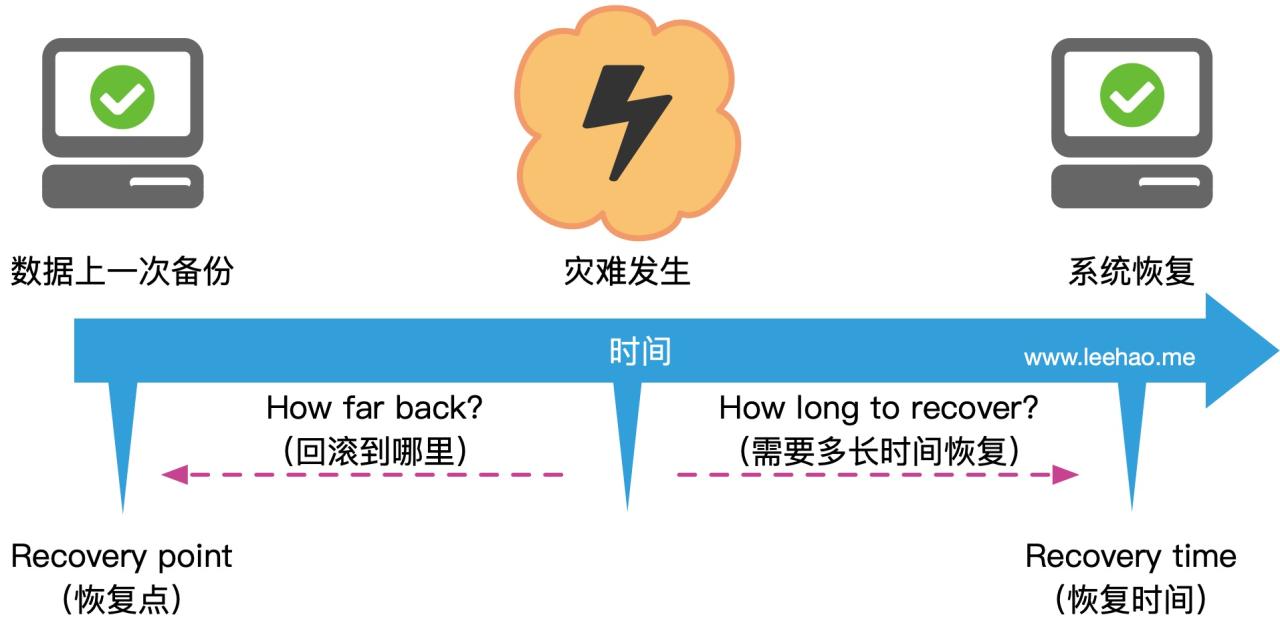
In conclusion, RPO and RTO are vital components of a robust disaster recovery plan. Understanding their definitions, the factors affecting them, and the process of establishing and measuring them is paramount for businesses of all sizes. This discussion highlights the importance of aligning disaster recovery strategies with specific RPO and RTO goals, considering the impact of technology and business priorities.
By carefully defining and managing these metrics, organizations can minimize data loss and downtime, ensuring business continuity and operational resilience.
Questions Often Asked
What is the difference between RPO and RTO?
RPO (Recovery Point Objective) defines the maximum acceptable amount of data loss after a disaster, measured in time. RTO (Recovery Time Objective) defines the maximum acceptable amount of downtime after a disaster, also measured in time.
How do business priorities influence RPO and RTO?
Business priorities directly impact the determination of RPO and RTO. For example, a financial institution with stringent regulatory requirements might have a lower tolerance for data loss and downtime compared to a retail company. This directly affects the recovery strategies employed.
What are some common metrics for evaluating disaster recovery performance?
Common metrics include recovery time, data loss, restoration time, and the frequency of successful tests. These provide a clear picture of how well the disaster recovery plan is functioning and its adherence to RPO and RTO goals.
How does cloud computing impact RPO and RTO?
Cloud-based solutions can significantly reduce RTO and RPO by offering quick access to data and applications. However, specific considerations, such as data replication strategies and vendor SLAs, need to be carefully addressed.