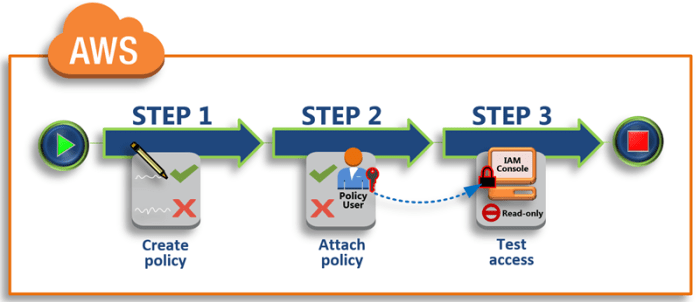
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) has become increasingly vital in today’s digital landscape. It’s a comprehensive approach to ensuring the security of your cloud environments, encompassing everything from configuration assessments to continuous monitoring and automated remediation. As organizations increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud, understanding and implementing effective CSPM strategies is no longer optional; it’s a fundamental requirement for safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining business continuity.
This discussion will explore the core principles of CSPM, its key components, and the tangible benefits it offers. We’ll delve into how CSPM solutions integrate with leading cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP, examining common use cases and practical implementation strategies. Furthermore, we’ll address the challenges organizations face in adopting CSPM and provide insights into the future of this evolving field, ensuring you’re well-equipped to navigate the complexities of cloud security.
Defining Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is a critical component of a robust cloud security strategy. It helps organizations understand and manage their security risk across their cloud environments. CSPM tools and practices are designed to continuously assess, identify, and remediate security vulnerabilities and misconfigurations, ensuring a strong security posture.
Core Purpose of CSPM in Cloud Environments
The core purpose of CSPM is to automate and streamline the process of securing cloud environments. It focuses on maintaining and improving an organization’s security posture by proactively identifying and addressing security weaknesses.CSPM achieves this through:
- Continuous Monitoring: Constantly scanning cloud environments for misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and compliance violations.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the potential impact of identified security issues.
- Remediation: Providing guidance and automated actions to fix security problems.
- Compliance Enforcement: Ensuring adherence to industry regulations and internal security policies.
Concise Definition of CSPM for a Non-Technical Audience
CSPM can be simply described as a system that helps businesses keep their cloud environments secure. It’s like having a security guard constantly watching over your cloud infrastructure, identifying potential problems, and suggesting ways to fix them. This ensures data and applications stored in the cloud are protected from threats.
Differences Between CSPM and Traditional Security Approaches
Traditional security approaches often rely on perimeter-based security, focusing on protecting the network edge. However, cloud environments operate differently, with dynamic resources and distributed workloads. CSPM adapts to these differences.Here’s how CSPM differs:
- Focus: Traditional security often focuses on hardware and network security, while CSPM emphasizes cloud-specific configurations and vulnerabilities.
- Scope: Traditional security might protect a physical data center, whereas CSPM covers multiple cloud providers and services.
- Automation: CSPM leverages automation to continuously monitor and remediate security issues, unlike the manual processes often used in traditional security.
- Visibility: CSPM provides a centralized view of the security posture across all cloud resources, a feature often lacking in traditional approaches.
CSPM provides a proactive and automated approach to cloud security, which is essential for organizations migrating to or operating in the cloud. It’s designed to address the unique challenges of cloud environments, offering greater visibility, agility, and effectiveness compared to traditional security methods.
Key Components of CSPM
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) solutions are built upon several core components that work in concert to provide comprehensive security and compliance for cloud environments. These components are essential for organizations seeking to proactively identify and mitigate risks, enforce security policies, and maintain a strong security posture.
Configuration Assessment
Configuration assessment is a critical function within CSPM, focused on evaluating the security settings of cloud resources. This involves comparing the current configurations against established security benchmarks, industry best practices, and internal policies.
Configuration assessment typically involves:
- Automated Scanning: CSPM tools automatically scan cloud environments to identify and analyze the configurations of various resources, such as virtual machines, storage buckets, databases, and network settings. This automated process significantly reduces the manual effort required for security assessments.
- Policy Enforcement: The tools enforce predefined security policies and compliance requirements. For example, a policy might require all S3 buckets to be encrypted, or that specific ports on virtual machines are closed.
- Benchmarking: CSPM solutions often incorporate industry-standard benchmarks, such as those from the Center for Internet Security (CIS) or the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). These benchmarks provide a baseline for secure configurations and help organizations ensure they are meeting recognized security standards.
- Reporting and Remediation: CSPM tools generate detailed reports that highlight misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and compliance violations. These reports often include recommendations for remediation, helping security teams prioritize and address issues effectively.
For example, a CSPM solution might detect that a publicly accessible S3 bucket is storing sensitive data. The tool would then alert the security team, providing details on the misconfiguration and suggesting steps to restrict access, such as changing the bucket’s permissions to private. Another example is the detection of misconfigured firewall rules that expose critical services to the public internet, allowing potential attackers to gain access.
Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is a fundamental aspect of CSPM, providing ongoing visibility into the security posture of cloud environments. This involves the constant collection, analysis, and interpretation of security-related data to detect threats, identify vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance.
Continuous monitoring involves:
- Real-time Data Collection: CSPM tools continuously collect data from various sources, including cloud provider APIs, security logs, and vulnerability scanners. This real-time data provides a comprehensive view of the cloud environment’s security status.
- Threat Detection: CSPM solutions use various techniques, such as anomaly detection and behavior analysis, to identify potential threats. These tools can detect unusual activity, such as unauthorized access attempts or suspicious network traffic.
- Vulnerability Scanning: CSPM tools regularly scan cloud resources for known vulnerabilities, such as outdated software or misconfigured security settings. This proactive approach helps organizations identify and address weaknesses before they can be exploited.
- Compliance Monitoring: CSPM tools continuously monitor the cloud environment to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and internal security policies. This includes tracking changes to configurations, monitoring access controls, and verifying that security controls are in place.
- Alerting and Incident Response: CSPM solutions generate alerts when they detect security incidents or compliance violations. These alerts enable security teams to respond quickly and effectively to threats and ensure that issues are addressed promptly.
For instance, consider a scenario where a CSPM solution detects an unusual spike in network traffic originating from an unfamiliar IP address. The tool would generate an alert, prompting the security team to investigate the activity. The investigation might reveal that the traffic is malicious, indicating a potential distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack or an attempt to exploit a vulnerability. Another case is the monitoring of data access patterns.
If a CSPM solution detects an unusual pattern of data access, such as a user accessing sensitive data outside of normal business hours, it can trigger an alert to investigate potential data exfiltration.
Benefits of Implementing CSPM
Adopting a Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) solution offers significant advantages for organizations leveraging cloud services. These benefits span enhanced security, improved efficiency, and cost savings, ultimately leading to a more robust and resilient cloud environment. The implementation of CSPM represents a proactive approach to cloud security, enabling organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Enhanced Security and Risk Reduction
CSPM significantly strengthens cloud security posture by continuously monitoring and assessing cloud environments for misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and compliance violations. This proactive approach minimizes the attack surface and reduces the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. Real-time monitoring and automated remediation capabilities enable organizations to quickly address security issues as they arise, limiting the potential impact of security threats.
Improved Efficiency and Automation
CSPM automates many manual security tasks, such as configuration reviews, compliance checks, and vulnerability assessments. This automation streamlines security operations, freeing up security teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. CSPM tools integrate with cloud platforms, allowing for automated remediation of security issues, such as misconfigured security groups or overly permissive access controls. This automation reduces the time and effort required to maintain a secure cloud environment.
Cost Benefits of CSPM versus Manual Security Processes
Compared to manual security processes, CSPM offers substantial cost savings. Manual processes are time-consuming, error-prone, and often require significant human resources. CSPM automates these processes, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing the risk of human error. The cost savings associated with CSPM include reduced labor costs, decreased downtime, and lower expenses related to security incidents. The reduction in security incidents also helps to avoid potentially high costs of data breaches and regulatory fines.Consider a hypothetical scenario: A company with a manual security process spends an estimated 40 hours per week on configuration reviews and compliance checks, costing $4,000 per week in labor costs.
Implementing a CSPM solution that automates these tasks could reduce the time spent on these activities to 5 hours per week, resulting in a cost savings of $3,500 per week. This calculation only considers the direct labor cost and doesn’t include the benefits of improved security and reduced risk.
Compliance and Governance
CSPM simplifies compliance with industry regulations and internal security policies. It provides automated checks and reports to demonstrate compliance with frameworks such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR. This streamlines the audit process and reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties. CSPM also provides centralized visibility into cloud security posture, making it easier to manage and enforce security policies across all cloud resources.
Top 5 Reasons to Use CSPM
Organizations should use CSPM for a multitude of reasons, including the following:
- Continuous Monitoring and Assessment: CSPM provides ongoing monitoring of cloud environments, identifying and alerting on security vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in real-time. This proactive approach helps to mitigate risks before they can be exploited.
- Automated Remediation: CSPM solutions often offer automated remediation capabilities, allowing for the rapid correction of security issues. This reduces the time to resolve vulnerabilities and minimizes the potential for security incidents.
- Improved Compliance: CSPM simplifies compliance with industry regulations and internal security policies. Automated checks and reporting capabilities streamline the audit process and reduce the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Reduced Costs: CSPM automates many manual security tasks, reducing the need for human intervention and minimizing the risk of human error. This results in lower labor costs, decreased downtime, and reduced expenses related to security incidents.
- Enhanced Visibility and Control: CSPM provides a centralized view of cloud security posture, allowing organizations to gain greater visibility and control over their cloud environments. This improved visibility enables organizations to make more informed decisions about their cloud security strategy.
CSPM and Cloud Service Providers (CSPs)
CSPM solutions are designed to seamlessly integrate with various cloud service providers, enabling organizations to manage and secure their cloud environments effectively. This integration is crucial because it allows CSPM tools to gather data, analyze configurations, and enforce security policies across different platforms. The degree of integration and the specific features supported can vary depending on the CSP and the CSPM vendor.
Integration with Cloud Service Providers
CSPM’s functionality is greatly enhanced through its ability to integrate with leading cloud platforms. These integrations enable the CSPM tool to collect data, assess security configurations, and implement security policies consistently across multiple cloud environments. The integration methods often involve APIs and specific cloud provider services.CSPM tools leverage APIs provided by cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) to access configuration data, security logs, and other relevant information.
This data is then analyzed to identify misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and compliance violations. This approach allows CSPM to maintain a unified security posture, regardless of the underlying cloud infrastructure. For example, a CSPM tool can use the AWS Security Hub API to retrieve security findings from AWS services and correlate them with other data sources. Similarly, it can use the Azure Security Center API to access security recommendations and alerts.
CSPM Features Across Different CSPs
The features offered by CSPM tools can vary depending on the specific cloud service provider. However, most tools provide core functionalities across different platforms, while also offering provider-specific features.Below is a table that illustrates how CSPM features are typically implemented across AWS, Azure, and GCP:
| Feature | AWS | Azure | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration Monitoring | Monitors AWS resource configurations using services like AWS Config and CloudTrail. | Monitors Azure resource configurations using Azure Policy and Azure Monitor. | Monitors GCP resource configurations using Cloud Asset Inventory and Cloud Audit Logs. |
| Compliance Management | Supports compliance with standards like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and CIS benchmarks using AWS Config Rules and Security Hub. | Supports compliance with standards like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and CIS benchmarks using Azure Policy and Security Center. | Supports compliance with standards like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and CIS benchmarks using Security Command Center and Policy. |
| Vulnerability Scanning | Integrates with vulnerability scanners and analyzes security findings from AWS services like Inspector. | Integrates with vulnerability scanners and analyzes security findings from Azure Security Center. | Integrates with vulnerability scanners and analyzes security findings from Security Command Center. |
| Threat Detection | Leverages AWS CloudTrail, CloudWatch, and GuardDuty to detect and respond to threats. | Leverages Azure Security Center and Sentinel to detect and respond to threats. | Leverages Security Command Center and Chronicle Security to detect and respond to threats. |
Examples of CSPM Tools and Their Integrations
Several CSPM tools offer comprehensive integrations with major cloud providers, providing robust security management capabilities. The degree of integration and the specific features supported can vary depending on the CSP and the CSPM vendor.
- CloudCheckr: CloudCheckr is a CSPM tool that provides deep integrations with AWS, Azure, and GCP. It offers automated security assessments, compliance monitoring, and remediation recommendations. For example, it can automatically detect misconfigurations in AWS S3 buckets or Azure storage accounts. It uses APIs to pull configuration data, security logs, and other relevant information from the cloud providers.
- Orca Security: Orca Security focuses on agentless cloud security, providing visibility and security across AWS, Azure, and GCP. It analyzes cloud assets for vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance issues without the need for agents. For instance, Orca can identify exposed data in AWS S3 buckets by scanning the buckets’ permissions and content. Orca uses read-only APIs to gather data, reducing the impact on cloud resources.
- Wiz: Wiz is a cloud security platform that offers integrations with AWS, Azure, and GCP. It provides a comprehensive view of cloud risks, including vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance violations. For example, Wiz can identify publicly accessible virtual machines in Azure or misconfigured IAM roles in GCP. It relies on cloud provider APIs for data collection and analysis.
Common CSPM Use Cases
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) offers a robust framework for addressing a wide range of cloud security challenges. Its effectiveness stems from its ability to proactively identify and remediate vulnerabilities, ensuring a strong security posture across diverse cloud environments. CSPM’s versatility makes it applicable in various scenarios, from maintaining compliance to responding to real-time security threats.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Meeting compliance and regulatory requirements is a significant use case for CSPM. Organizations must adhere to various standards and regulations, such as HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, and ISO 27001, depending on their industry and the data they handle. CSPM tools streamline this process by automating the assessment of cloud configurations against these standards.CSPM tools provide several key capabilities in this area:
- Automated Compliance Checks: CSPM solutions continuously scan cloud environments, comparing configurations against predefined compliance benchmarks. These benchmarks are often built-in for common regulations or can be customized to meet specific organizational needs.
- Real-time Monitoring: CSPM provides real-time monitoring of cloud resources, detecting deviations from compliance policies as they occur. This allows for immediate remediation efforts.
- Reporting and Auditing: CSPM generates detailed reports on compliance status, including identified violations and recommended remediation steps. These reports are invaluable for audits and demonstrating adherence to regulations.
- Remediation Guidance: When non-compliance is detected, CSPM often provides automated remediation guidance or, in some cases, can automatically fix the misconfigurations, reducing the time and effort required to achieve compliance.
For example, a healthcare provider using AWS might utilize CSPM to ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations. The CSPM tool would automatically check configurations for encryption of data at rest, proper access controls, and regular security audits. If a misconfiguration is detected, such as an unencrypted S3 bucket containing protected health information (PHI), the CSPM tool would alert the security team and provide guidance on how to encrypt the bucket.
This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and associated penalties.
Detecting and Responding to Misconfigurations
Misconfigurations are a leading cause of cloud security incidents. These errors can range from simple mistakes, such as leaving a port open, to more complex issues, such as improper access controls. CSPM plays a critical role in identifying and mitigating these risks.CSPM’s effectiveness in this area stems from its ability to:
- Continuous Monitoring: CSPM tools continuously monitor cloud environments, scanning for misconfigurations across various services and resources. This ongoing monitoring ensures that any changes that introduce vulnerabilities are quickly identified.
- Automated Detection: CSPM solutions use a combination of rule-based detection, anomaly detection, and machine learning to identify misconfigurations. Rule-based detection identifies violations of predefined security best practices, while anomaly detection identifies unusual behavior that may indicate a misconfiguration.
- Prioritization of Risks: CSPM tools prioritize identified misconfigurations based on their severity and potential impact. This helps security teams focus their remediation efforts on the most critical issues first.
- Remediation Capabilities: Many CSPM tools offer automated remediation capabilities, allowing them to automatically fix misconfigurations, such as closing open ports or adjusting access controls. This significantly reduces the time and effort required to address security vulnerabilities.
A specific use case involves a company using AWS to host its web application. The company’s CSPM tool continuously monitors its infrastructure for misconfigurations. The CSPM tool detects that a security group, which controls inbound traffic to a critical web server, has a rule that allows unrestricted access from any IP address (0.0.0.0/0) on port 22 (SSH). This is a significant security risk, as it allows unauthorized users to potentially gain access to the server.
The CSPM tool alerts the security team about the misconfiguration. The team can then use the CSPM tool to automatically remove the problematic rule or follow the tool’s guidance to manually correct the configuration. This rapid response prevents a potential breach, demonstrating the value of CSPM in real-time security incident management.
CSPM Implementation Strategies
Implementing a Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) solution is a crucial step in fortifying your cloud environment. It requires a structured approach, careful configuration, and ongoing evaluation to ensure its effectiveness. This section provides a comprehensive guide to help you successfully deploy and manage a CSPM solution.
Step-by-Step Guide for Implementing a CSPM Solution
Implementing a CSPM solution involves several key steps. Following a structured approach ensures a smooth transition and optimal results.
- Define Objectives and Scope: Begin by clearly defining your security objectives. What specific cloud environments are you securing (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP)? What compliance regulations must you adhere to (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS)? Identify the critical assets and data you need to protect. This helps tailor the CSPM implementation to your specific needs.
- Select a CSPM Solution: Research and evaluate different CSPM tools based on your requirements. Consider factors such as features, integration capabilities, pricing, and vendor reputation. Some popular CSPM vendors include:
- CloudCheckr (now part of NetApp): Known for its comprehensive cloud security and compliance capabilities, including automated remediation.
- Orca Security: Offers a side-scanning approach that provides visibility into cloud assets and security risks without requiring agents.
- Wiz: Provides a platform for cloud security posture management, vulnerability management, and compliance.
- Onboard and Integrate: Integrate the chosen CSPM solution with your cloud accounts and services. This typically involves granting the CSPM tool appropriate permissions to access and analyze your cloud resources. Follow the vendor’s specific instructions for onboarding.
- Configure Security Policies and Baselines: Define and configure security policies and baselines based on industry best practices, compliance requirements, and your organization’s specific needs. Most CSPM tools offer pre-built policies, but you should customize them to align with your environment.
- Establish Baseline and Initial Assessment: Run an initial assessment to establish a baseline of your current security posture. This provides a snapshot of your existing vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
- Remediate Identified Issues: The CSPM tool will identify security risks and misconfigurations. Prioritize and remediate these issues based on their severity and potential impact. Many CSPM tools offer automated remediation capabilities.
- Implement Continuous Monitoring: Configure the CSPM tool to continuously monitor your cloud environment for security threats and misconfigurations. This involves setting up alerts and notifications to promptly address any issues.
- Refine and Optimize: Regularly review and refine your security policies, baselines, and configurations based on ongoing monitoring results and changes in your cloud environment. Adjust your approach as your cloud infrastructure evolves.
Best Practices for Configuring CSPM Tools Effectively
Configuring your CSPM tool effectively is critical to its success. This involves carefully considering the tool’s features and tailoring its settings to your specific environment.
- Customize Security Policies: While pre-built policies are helpful, customize them to align with your organization’s specific security requirements, compliance mandates, and risk tolerance. Don’t rely solely on default settings.
- Prioritize Alerts and Notifications: Configure alerts and notifications to be timely and relevant. Prioritize alerts based on the severity of the identified issues. Avoid alert fatigue by filtering out unnecessary noise.
- Automate Remediation Where Possible: Leverage the automation capabilities of your CSPM tool to automatically remediate common security issues, such as misconfigured security groups or open storage buckets.
- Integrate with Existing Security Tools: Integrate your CSPM tool with other security tools, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems and vulnerability scanners, to provide a comprehensive view of your security posture.
- Establish Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Define clear roles and responsibilities for managing and responding to security alerts and issues identified by the CSPM tool.
- Regularly Review and Update Configurations: Regularly review and update your CSPM tool’s configurations to ensure they remain relevant and effective as your cloud environment evolves. This includes updating policies, baselines, and alert thresholds.
Checklist for Evaluating the Success of a CSPM Implementation
Evaluating the success of your CSPM implementation is essential to ensure it’s meeting your security objectives. Use this checklist to assess the effectiveness of your solution.
- Reduced Number of Security Incidents: Track the number of security incidents before and after implementing the CSPM solution. A successful implementation should result in a reduction in incidents.
- Improved Compliance Posture: Regularly assess your compliance posture against relevant regulations (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS). The CSPM tool should help you achieve and maintain compliance.
- Faster Incident Response Times: Measure the time it takes to identify and respond to security incidents. CSPM tools should enable faster incident response times.
- Increased Visibility into Cloud Security Risks: Evaluate the level of visibility you have into your cloud environment. The CSPM tool should provide comprehensive visibility into potential risks and vulnerabilities.
- Improved Security Team Efficiency: Assess the efficiency of your security team. The CSPM tool should automate tasks and free up your team to focus on more strategic security initiatives.
- Reduced Costs Associated with Security: Evaluate if the CSPM solution has helped you optimize cloud security spending, potentially reducing costs related to manual security efforts or remediation.
- Regularly Updated Security Posture Reports: Ensure the CSPM tool generates comprehensive reports on your cloud security posture. These reports should provide valuable insights into your security performance.
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Gather feedback from stakeholders, including security teams, compliance officers, and IT administrators, to assess their satisfaction with the CSPM solution.
CSPM Tools and Technologies
The effectiveness of Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) relies heavily on the tools and technologies used to automate security assessments, identify vulnerabilities, and enforce security policies across cloud environments. Selecting the right CSPM tools is crucial for organizations to achieve and maintain a robust cloud security posture. This section explores the landscape of available CSPM tools and provides insights into their features and functionalities.
Popular CSPM Tools Available in the Market
Several CSPM tools are available, each offering a unique set of features and capabilities. Understanding the prominent players in the CSPM market helps organizations choose the best fit for their specific needs. Some of the leading CSPM tools include:
- CloudHealth by VMware: Known for its cloud cost management and security capabilities, CloudHealth provides a comprehensive view of cloud environments.
- Orca Security: Orca Security offers agentless cloud security, providing visibility and threat detection across various cloud services.
- Prisma Cloud by Palo Alto Networks: A comprehensive cloud security platform that offers CSPM, cloud workload protection, and compliance management.
- Wiz: Wiz is a cloud security platform that focuses on agentless visibility, risk prioritization, and remediation guidance.
- Dome9 by Check Point: Dome9 provides cloud security posture management, compliance, and automation capabilities for multi-cloud environments.
- Qualys Cloud Security: Qualys offers cloud security posture management as part of its broader security and compliance platform.
- Lacework: Lacework provides cloud security through data-driven insights and automated threat detection.
Comparing Different CSPM Tool Features and Functionalities
Different CSPM tools have varied strengths. Comparing their features and functionalities is essential to make an informed decision. The following table provides a comparison of features across several CSPM tools:
| Feature | CloudHealth by VMware | Orca Security | Prisma Cloud by Palo Alto Networks | Wiz |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agentless Scanning | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Multi-Cloud Support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Compliance Reporting | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Vulnerability Scanning | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Threat Detection | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Automated Remediation | Limited | Limited | Yes | Limited |
| Cost Optimization | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Integration with CI/CD pipelines | Limited | Limited | Yes | Limited |
Example of a CSPM Tool’s Dashboard, Describing Its Key Elements
CSPM tools typically present their findings through a dashboard that provides a centralized view of the cloud security posture. This dashboard usually includes various elements to help security teams understand and address security risks.Let’s consider a simplified example of a CSPM dashboard. Imagine the dashboard is provided by a fictional CSPM tool called “CloudSecure”.The CloudSecure dashboard would likely include the following key elements:
- Overall Security Score: A numerical score representing the organization’s overall cloud security posture. This score is often calculated based on the severity and number of identified vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance violations.
- Risk Summary: A summary of the most critical security risks identified in the cloud environment. This might include a list of the top vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, or compliance violations.
- Compliance Status: A view of the organization’s compliance with various industry standards and regulatory frameworks (e.g., CIS Benchmarks, PCI DSS, HIPAA). This section displays the status of compliance checks and identifies any non-compliant resources.
- Resource Inventory: A list of all cloud resources discovered and monitored by the CSPM tool. This provides visibility into the assets within the cloud environment.
- Alerts and Notifications: Real-time alerts and notifications about security incidents, vulnerabilities, and misconfigurations. Alerts are often categorized by severity level (e.g., critical, high, medium, low) to prioritize remediation efforts.
- Trending Analysis: Graphs and charts that show trends in security posture over time. This can help identify areas where security is improving or deteriorating.
- Remediation Guidance: Recommendations and steps to address identified vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. The tool often provides specific instructions or automated scripts to help security teams fix issues.
The dashboard is designed to be intuitive and actionable, allowing security teams to quickly understand the organization’s security posture, identify critical risks, and take steps to remediate vulnerabilities.
Challenges in CSPM Adoption
Adopting Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is a significant undertaking, and organizations often encounter several hurdles. Understanding these challenges and proactively addressing them is crucial for a successful CSPM implementation. Successfully navigating these obstacles ensures the organization can effectively leverage CSPM to enhance its cloud security posture.
Complexity of Cloud Environments
The inherent complexity of cloud environments presents a major challenge. Cloud infrastructures, with their diverse services, configurations, and constantly evolving nature, make it difficult to gain complete visibility and control. This complexity can hinder the effective implementation of CSPM solutions.
- Diverse Cloud Services: Organizations often utilize a wide array of cloud services, from compute and storage to databases and networking. Each service has its own security configurations and best practices, increasing the complexity of managing security posture.
- Dynamic Environments: Cloud environments are highly dynamic. Resources are frequently provisioned, de-provisioned, and modified, requiring continuous monitoring and adaptation of security policies.
- Configuration Drift: Misconfigurations and changes to cloud resources over time can lead to configuration drift, where the actual security posture deviates from the intended baseline. This can introduce vulnerabilities and security risks.
Lack of Skilled Personnel
A shortage of skilled personnel is a significant obstacle to CSPM adoption. Implementing and managing CSPM solutions effectively requires expertise in cloud security, cloud platforms, and security automation. The demand for these skills often outstrips the available supply.
- Cloud Security Expertise: Organizations need professionals with deep knowledge of cloud security principles, best practices, and common vulnerabilities.
- Platform-Specific Knowledge: Expertise in specific cloud platforms (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP) is essential to configure and manage CSPM tools effectively.
- Automation and Scripting Skills: The ability to automate security tasks and integrate CSPM with other security tools is crucial for efficiency and scalability.
Integration Challenges
Integrating CSPM with existing security tools and processes can be challenging. Organizations must ensure that CSPM solutions seamlessly integrate with their Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, vulnerability scanners, and other security tools.
- SIEM Integration: Integrating CSPM with SIEM systems is critical for centralized logging, monitoring, and incident response. This allows security teams to correlate CSPM findings with other security events.
- API Integration: CSPM tools should integrate with cloud provider APIs to collect data, automate remediation, and enforce security policies.
- Workflow Integration: Integrating CSPM into existing security workflows, such as incident response and change management, is essential for efficient operations.
Resistance to Change
Organizational resistance to change can hinder CSPM adoption. Implementing a new security solution often requires changes to existing processes, roles, and responsibilities, which can be met with resistance from various stakeholders.
- Lack of Awareness: A lack of understanding about the benefits of CSPM can lead to resistance. Educating stakeholders about the value of CSPM is crucial.
- Process Changes: Implementing CSPM often requires changes to existing security processes, such as configuration management and incident response.
- Fear of Disruption: Some stakeholders may fear that CSPM will disrupt their workflows or introduce new challenges.
Cost Considerations
Cost is another significant factor that organizations must consider. Implementing and maintaining CSPM solutions involves various costs, including the cost of the tools, training, and personnel.
- Tooling Costs: CSPM solutions can range in price, from open-source tools to enterprise-grade platforms. Organizations must carefully evaluate their needs and budget when selecting a CSPM tool.
- Implementation Costs: Implementing CSPM requires time and effort, including configuring the tool, integrating it with existing systems, and training personnel.
- Operational Costs: Ongoing costs include maintenance, monitoring, and updates.
Data Overload and Alert Fatigue
CSPM tools can generate a large volume of security alerts, leading to data overload and alert fatigue. Security teams must be able to effectively filter and prioritize these alerts to focus on the most critical risks.
- High Volume of Alerts: CSPM tools can generate a large number of alerts, especially in complex cloud environments.
- Prioritization Challenges: Prioritizing alerts based on risk and impact is crucial to avoid alert fatigue.
- False Positives: CSPM tools can sometimes generate false positive alerts, which can waste time and resources.
The Future of CSPM

Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is not static; it’s a dynamic field constantly evolving to meet the challenges of an ever-changing cloud landscape. As cloud adoption continues to accelerate, so too will the sophistication and capabilities of CSPM solutions. This section explores the evolving trends, the impact of emerging technologies, and the future integration of CSPM with other security solutions.
Evolving Trends in Cloud Security Posture Management
Several key trends are shaping the future of CSPM, driving innovation and influencing its capabilities. These trends reflect the increasing complexity of cloud environments and the growing sophistication of cyber threats.
- Increased Automation and Orchestration: Automation will become even more central to CSPM. Solutions will leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to automatically detect, analyze, and remediate security misconfigurations and vulnerabilities. This includes automated policy enforcement, incident response, and compliance checks. For example, a CSPM solution might automatically quarantine a compromised virtual machine based on pre-defined rules.
- Shift-Left Security and DevSecOps Integration: CSPM will increasingly integrate into the software development lifecycle (SDLC). This involves incorporating security checks and posture assessments earlier in the development process, a concept known as “shift-left security.” This integration will support DevSecOps practices, enabling developers to identify and fix security issues before deployment, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities in production.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Support: Organizations are increasingly adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies. CSPM solutions will need to provide comprehensive visibility and control across these diverse environments, offering consistent security policies and compliance management across all platforms. This necessitates CSPM solutions that support a wide range of cloud providers and on-premises infrastructure.
- Focus on Real-Time Threat Detection and Response: CSPM will evolve to incorporate real-time threat detection capabilities, leveraging advanced analytics and threat intelligence to identify and respond to active threats. This includes analyzing cloud activity logs, network traffic, and other data sources to detect malicious behavior and automatically trigger remediation actions.
- Emphasis on User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): CSPM will incorporate UEBA to identify anomalous user and entity behavior within cloud environments. This involves analyzing user activity patterns, access requests, and other data points to detect insider threats, compromised accounts, and other malicious activities.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on CSPM
Emerging technologies are poised to significantly impact the future of CSPM, enhancing its capabilities and transforming how organizations manage cloud security posture.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML will play a pivotal role in automating security tasks, improving threat detection, and enhancing risk assessment. ML algorithms can be trained to identify and predict security threats based on historical data and patterns. AI can automate remediation actions, such as automatically applying security patches or reconfiguring cloud resources.
- Serverless Computing Security: As serverless computing becomes more prevalent, CSPM solutions will need to adapt to secure these dynamic and ephemeral environments. This includes providing visibility into serverless functions, ensuring proper configuration, and detecting vulnerabilities in serverless code.
- Container Security: Containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes are transforming application deployment. CSPM solutions will need to offer robust container security capabilities, including vulnerability scanning, configuration management, and runtime protection.
- Quantum Computing: While quantum computing is still in its early stages, it poses a significant threat to current cryptographic methods. CSPM solutions will need to prepare for the post-quantum era by incorporating quantum-resistant cryptography and developing strategies to mitigate the risks associated with quantum attacks.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain could be used to secure CSPM data, ensuring the integrity and immutability of security logs and configuration data. This can help prevent tampering and provide a verifiable audit trail for compliance purposes.
Future Integration of CSPM with Other Security Solutions
The future of CSPM involves seamless integration with other security solutions to create a unified and comprehensive security ecosystem. This integration will enhance visibility, improve threat detection, and streamline security operations.
- Integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: CSPM solutions will integrate with SIEM systems to provide a consolidated view of security events and incidents across the entire cloud environment. This integration will enable security teams to correlate CSPM findings with other security data, such as network logs and endpoint data, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of security threats.
- Integration with Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): CSPM and CASB solutions will integrate to provide comprehensive security for cloud applications and data. CSPM can monitor the security posture of the cloud infrastructure, while CASBs can enforce security policies for cloud applications and user access.
- Integration with Vulnerability Management Systems: CSPM will integrate with vulnerability management systems to provide a holistic view of vulnerabilities across the cloud environment. This will allow organizations to prioritize remediation efforts based on the severity of vulnerabilities and the impact on the overall security posture.
- Integration with Incident Response Platforms: CSPM solutions will integrate with incident response platforms to automate incident handling and remediation. When a security incident is detected, the CSPM solution can automatically trigger incident response workflows, such as isolating affected resources, notifying security teams, and collecting forensic data.
- API-Driven Integration: A key aspect of future integration is the use of APIs. CSPM solutions will provide robust APIs to enable seamless integration with other security tools and platforms. This will allow organizations to build customized security workflows and automate security tasks.
Epilogue
In summary, Cloud Security Posture Management is essential for robust cloud security. From understanding its core components and implementation strategies to recognizing its integration with cloud providers and anticipating future trends, CSPM empowers organizations to proactively identify and mitigate security risks. By embracing CSPM, businesses can confidently leverage the benefits of the cloud while maintaining a strong security posture, ensuring their digital assets remain protected and their operations resilient.
Remember that continuous vigilance and adaptation are key to thriving in the ever-evolving world of cloud security.
Questions Often Asked
What exactly does CSPM do?
CSPM continuously monitors your cloud environment for misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and compliance violations, providing automated alerts and remediation recommendations to strengthen your security posture.
How does CSPM differ from a Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)?
While both enhance cloud security, CSPM focuses on the security of the cloud infrastructure itself (configurations, compliance), while CASB primarily addresses security around user access and data in the cloud.
Can CSPM automate security tasks?
Yes, CSPM solutions often automate tasks such as vulnerability scanning, compliance checks, and even remediation actions like fixing misconfigurations, saving time and reducing manual effort.
Is CSPM only for large enterprises?
No, CSPM solutions are scalable and can be tailored to organizations of all sizes. Even small businesses can benefit from the automated security and compliance features CSPM provides.